What is the role of testing the COAGs of a patient on NOACs?
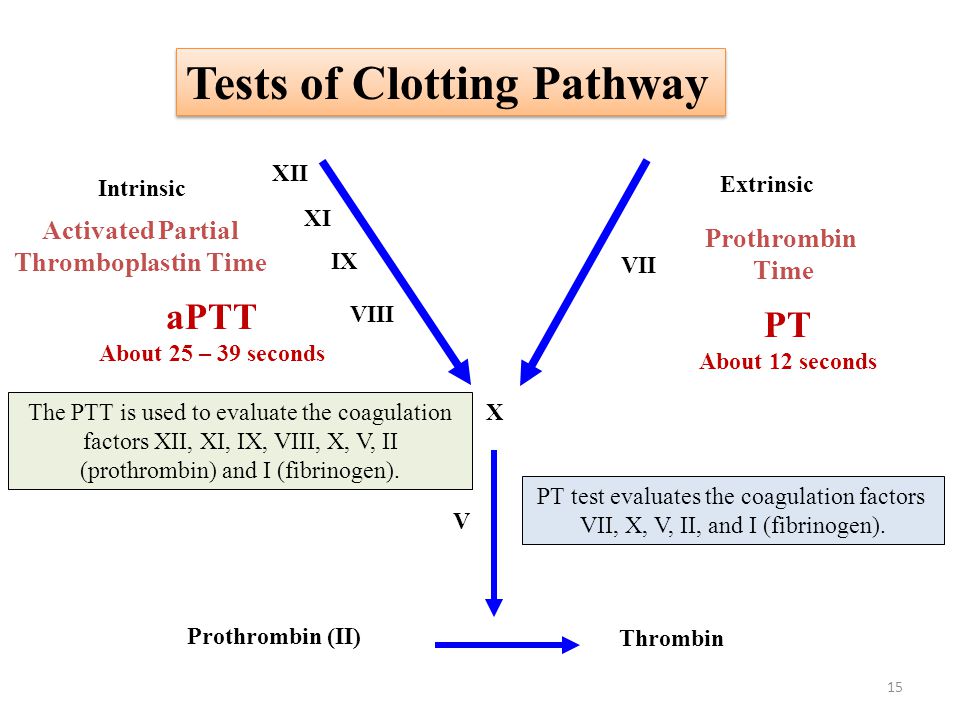
Review: the coagulation cascade and PT/PTT
*Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin and the time it takes is the TT (normal is < 20 seconds).
NOAC = Novel oral anticoagulants
Thrombin inhibitor
Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
Factor Xa inhibitors
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
Apixaban (Eliquis)
Edoxaban (Savaysa)
*Warfarin is a vitamin K antagonist affecting factors II (prothrombin), VII, IX, X and proteins C, S, and Z
Where NOACs affect the coagulation cascade
The takeaway…
NOAC levels are difficult to monitor.
With dabigatran, a normal PTT can reassure you the patient is not supratherapeutic.
With rivaroxaban, a normal PT/INR can reassure you the patient is not supratherapeutic.
Otherwise coags may be elevated, but the values will not be of clinical utility.
Sources
Blann AD, Lip GYH. Laboratory Monitoring of the Non–Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(11):1140–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.07.010
Cuker A, Siegal DM, Crowther MA, Garcia DA. Laboratory measurement of the anticoagulant activity of the non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(11):1128–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.05.065
Noll, Andrew. Coagulation Assays and the New Oral Anticoagulants. American College of Cardiology June 22, 2015: https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/articles/2015/06/22/12/06/coagulation-assays-and-the-new-oral-anticoagulants
Thrombosis Canada. Use And Interpretation Of Laboratory Coagulation Tests In Patients Who Are Receiving A New Oral Anticoagulant (Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban, Apixaban). 2013: http://thrombosiscanada.ca/guides/pdfs/NOAC_Monitoring.pd